Balanced Cross Ply Laminate
Figure 1 10 a shows a typical tensile stress stain curve for a cross ply laminate.
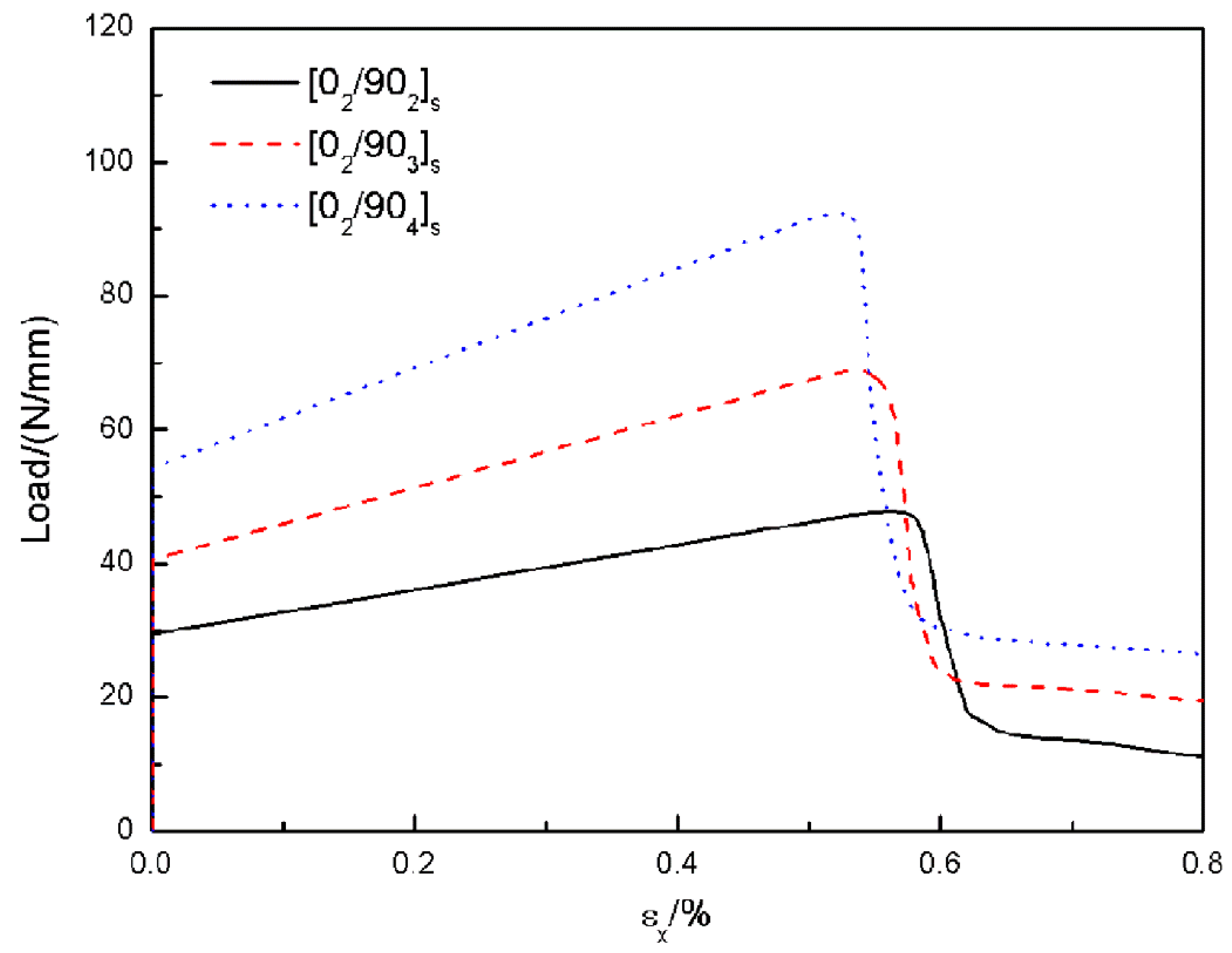
Balanced cross ply laminate. For cross ply laminates under quasi static loading fast fracture or crack onset rapid growth of the cracks usually occurs when the applied load or strain is typically 0 4 0 6. A laminate is balanced when it consists of pairs of layers of the same thickness and material where the angles of the plies are θand θ. Cross ply laminates for cross ply laminates a16 a26 b16 b26 d16 d 26 0. However the symmetry rule is shown to be a constraint that serves only to restrict the number of.
Thus a16 a26 0. If the laminate is not balanced and symmetric macro warpage will certainly occur during cool down. The study demonstrates that the common design rule of balanced and symmetric stacking sequences predominantly gives rise to bend twist coupling. Calculate the normal and shear stresses in the 0.
A balanced laminate is one that for every θ ply in the lay up there is an equivalent θ ply in the lay up. Js possessing mid plane symmetry is made of laminae having the el 15 gp glt 3 gpa e 6 gpa vuj 0 5 assume the total laminate thickness as unity. Cross ply and angle ply laminate specimens immersed in 45 c and 80 c temperature water for 80 days were tensile tested at 50 c 25 c and 50 c. An example of a balanced laminate is 0 45 45 90 45 45 0 whereas an unbalanced laminate would be 0 45.
For thin transverse plies i e thicknesses typically 0 25 mm the onset strain for matrix cracking can be delayed. The aged cross ply specimens figure 7 had nearly parallel strength temperature curves to the unaged but were reduced by 35 and 65 for 45 c and 80 c 80 days aging respectively the shear strength of the angle ply figure 8 is not reduced. All exceptions are presented in aiaa 2007 2083.